







Pure Vitamin C 1000mg Capsules
Powerful immune support and antioxidant protection in our pure-formula capsules.
- 1000mg high strength dosage per single capsule
- Pure, active ingredients without fillers or additives
- Ascorbic acid and sodium ascorbate for optimal absorption
- Specialised pullulan capsules for superior potency preservation
- Expertly manufactured and independently tested in the UK
- Each order plants a tree through Ecologi
90 Capsules | 1-3 Month Supply | Vegan
Choose options









What Makes Puramins Vitamin C Different?

Pure by Design
Unlike most supplements that contain unnecessary fillers, binders and additives, our supplements are completely free from these inactive ingredients. We carefully select only pure, active ingredients in their most effective form.
Learn More
Ingredients Optimised
We select only the most potent, scientifically-validated forms of nutrients. Each supplement is precisely formulated with optimal doses, carefully balanced for maximum benefit while adhering to UK safety guidelines.
Learn More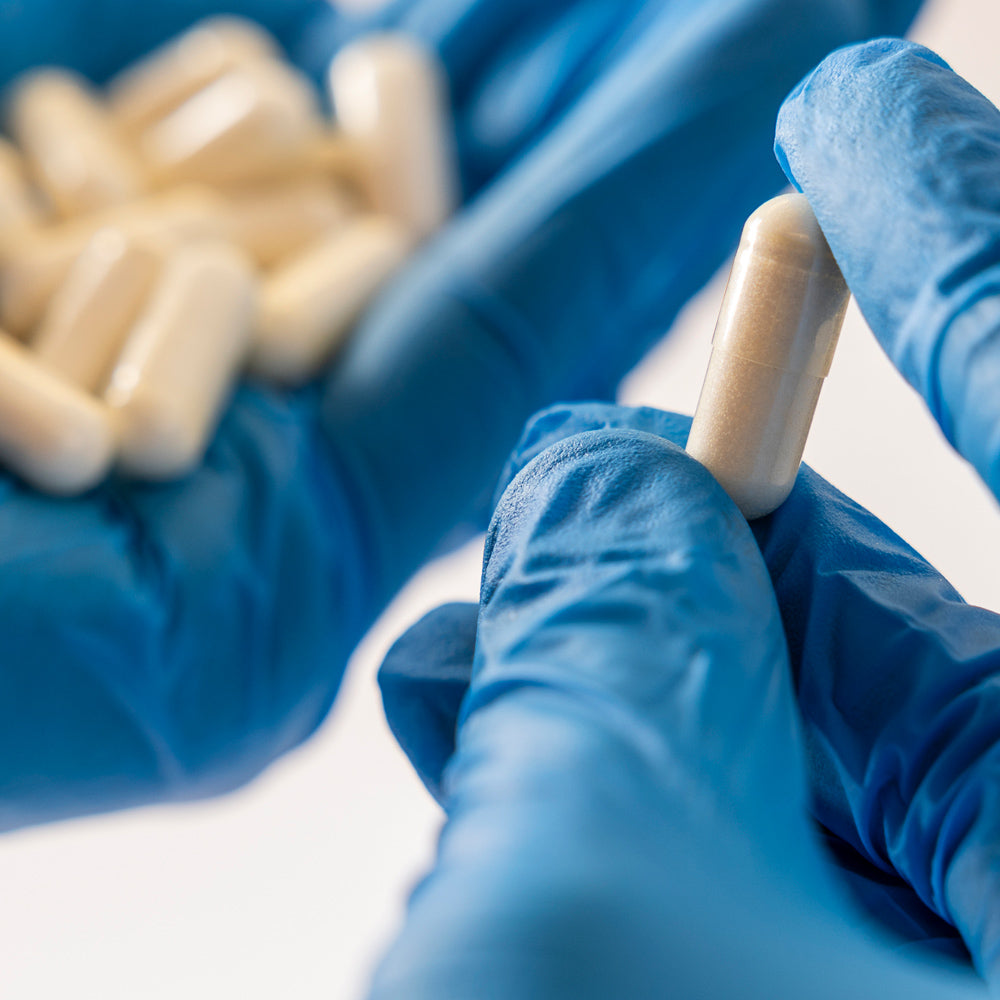
Quality Crafted
Quality manufacturing is essential for effective supplements. Our products are crafted in the UK under strict pharmaceutical-grade standards in ISO Class 8 clean rooms, partnering with a leading manufacturer with decades of experience.
Learn More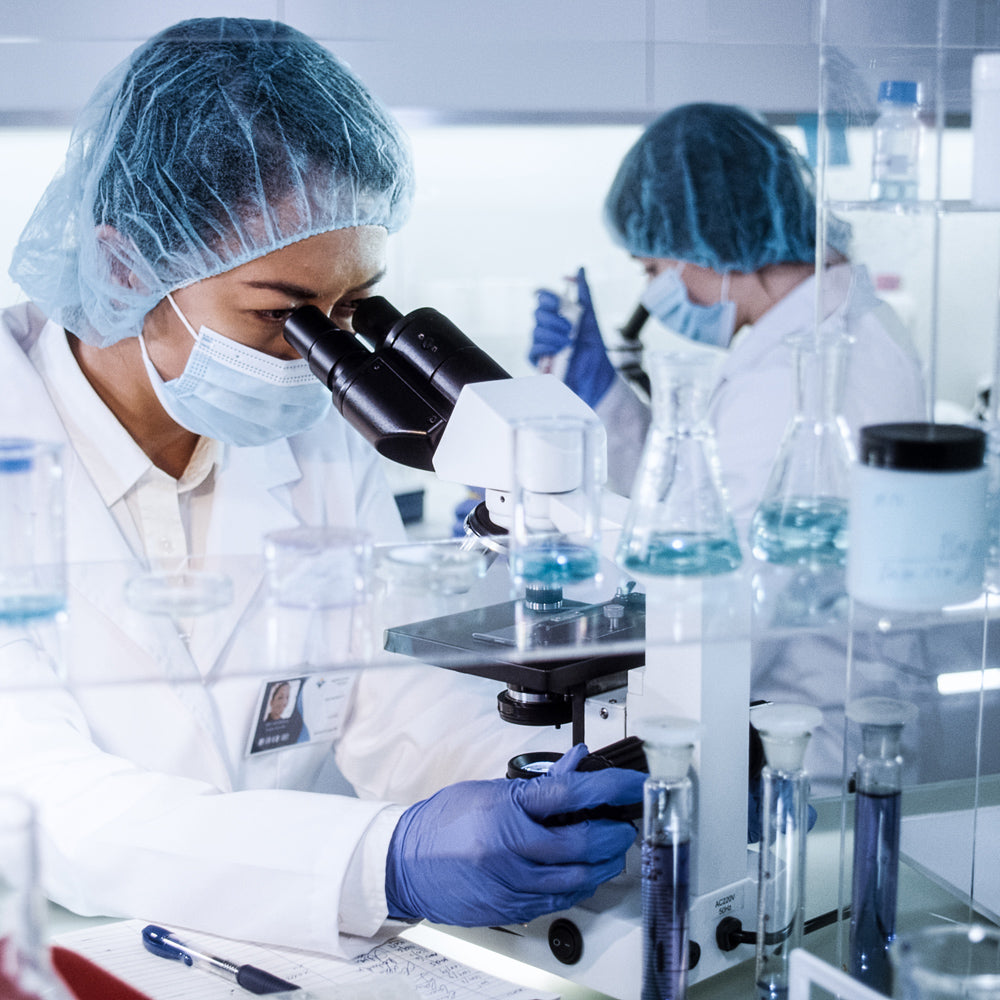
Transparency Assured
Every batch of our supplements undergoes rigorous third-party testing, ensuring what's on the label is exactly what's in the bottle. We provide clear, honest dosages and evidence-based formulas so you know precisely what you're putting into your body.
Learn More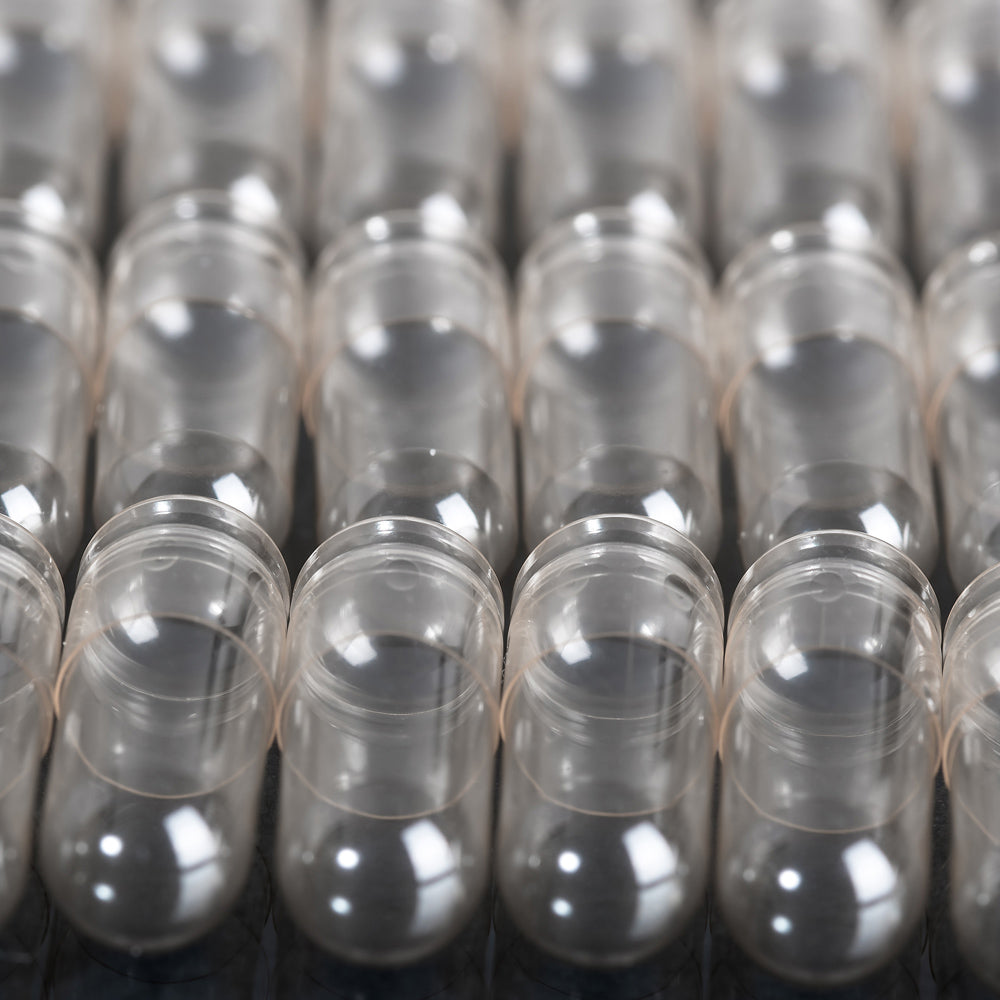
Capsules Redefined
We've reimagined supplement delivery with innovative pullulan capsules. Naturally fermented from fungi, they provide up to 300 times better oxygen protection than standard capsules while being environmentally conscious and prebiotic-supporting.
Learn More
Protecting the Planet Together
Our commitment to health extends beyond individual wellbeing. We use 30% recycled plastic bottles and manufacture our products with 100% renewable energy. Plus we also support global climate action by contributing to Ecologi with every order you make.
Learn More
Our Vitamin C Ingredients
Our vitamin C formula combines two complementary forms: 750mg of ascorbic acid and 250mg of sodium ascorbate.
Ascorbic acid, the primary form of vitamin C, is well-researched and highly effective at neutralising free radicals (2,3,4,5). As a weak acid, similar to the natural acidity in many fruits, it is combined with a slightly alkaline sodium ascorbate (sodium combined with Vitamin C), which offers sustained release properties and excellent bioavailability (6,7,8).
This balanced combination ensures optimal absorption while being well-tolerated by sensitive individuals.
Other mineral ascorbates, such as calcium, magnesium, potassium, zinc and manganese forms, while beneficial in providing additional minerals, can be expensive and risk mineral overload at higher doses. It is therefore more effective and safer to supplement these minerals separately if needed (9).

Benefits of Our Vitamin C
Immune System Support
Strengthens your body's natural defences and supports immune function during intense physical exercise*.
Collagen Formation
Supports the natural production of collagen for healthy skin, blood vessels, bones and gums*.
Energy & Vitality
Helps reduce tiredness and fatigue while supporting normal energy metabolism*.
Nervous System Function
Contributes to normal functioning of the nervous system and psychological function*.
Antioxidant Protection
Protects cells from oxidative stress, supports the regeneration of vitamin E and increases iron absorption*.
*Authorised EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) Health Claims (1).
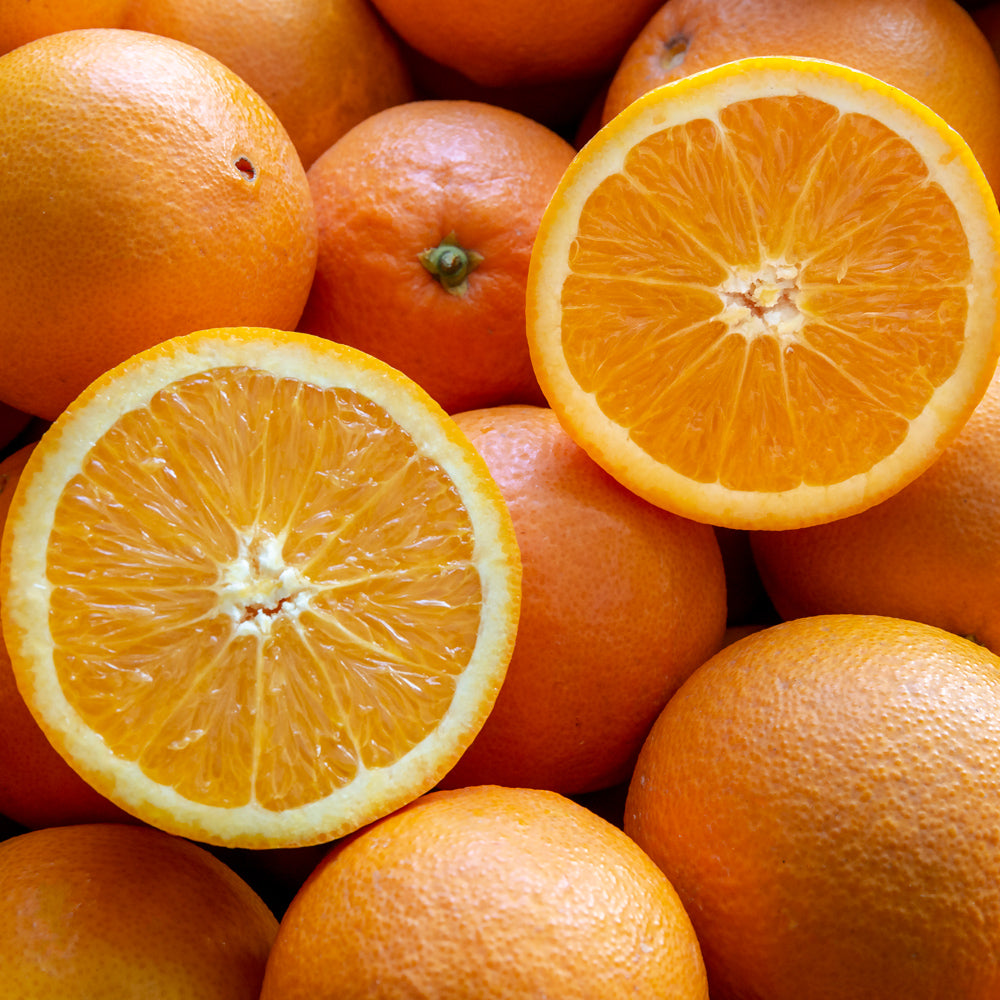

Why is Vitamin C Needed?
Unlike most mammals, humans cannot produce their own vitamin C. This essential nutrient must come from our diet or supplementation (2,10).
While a balanced diet typically includes vitamin C-rich foods, several modern factors make it increasingly challenging to maintain optimal levels through food alone (11,12).
Vitamin C is water-soluble, meaning our bodies cannot store it for long periods (10) and need a consistent daily intake to maintain healthy levels. This becomes particularly important during periods of stress, illness, or intense physical activity, when our bodies' demand for vitamin C increases significantly (13).
Our carefully formulated vitamin C supplement delivers 1000mg per capsule - equivalent to the vitamin C content of 14 oranges (14,15) - helping you maintain healthy levels regardless of dietary or lifestyle factors.
Product Information
Ingredients
Vitamin C 1000mg (1250% NRV*)
(as ascorbic acid) 750mg
(as sodium ascorbate) 250mg
Pullulan (capsule shell)
NRV = Nutrient Reference Value
Directions
Take 1-3 capsules daily with water or food, in divided doses, or as directed by a health professional. Do not exceed the recommended dose. Suitable for vegetarians and vegans.
Cautions
If you have any medical conditions, consult a health professional before use. Food supplements should not be used as substitute for a varied diet and healthy lifestyle. Use only if safety seal is intact. Store in a cool, dry place, out of reach and sight of children.
Common Vitamin C Questions
Is 'Natural' Vitamin C Better Than 'Synthetic'?
Over many decades, vitamin C has been a controversial ingredient. There have been many claims and counter-claims over which form of vitamin C is best, where it should come from and what actually real vitamin C is.
Some say that vitamin C from plants and fruits is the real thing as it's provided by nature and that factory made vitamin C is inferior and is not actual vitamin C. However as science shows, both natural and factory made forms are chemically identical, have the same biological activity and are equally well absorbed by the body (2,5,16,17,18,19,20). When you consume vitamin C from fruits and vegetables, you're getting the same active compound as from factory made vitamin c in supplements.
What is 'Food Grown' Vitamin C?
A very popular subject is that of 'food grown' vitamin C. This can be vitamin C grown in a food medium or cultured with yeast (21). The claim is that this process creates a more ‘natural’ form of vitamin C as it's bound to other food components.
However, it's important to understand that the end result is still ascorbic acid - the same molecule found in both regular supplements and fruits. While these products may contain additional food-based nutrients, the vitamin C itself is not fundamentally different (16,17,19). You often find that these products are significantly more expensive than standard vitamin C supplements, and require larger amounts of capsules to get the same amounts.
Do I Need A Vitamin C 'Complex'?
Perhaps the most common question is that people believe ascorbic acid isn't vitamin C at all, it is in fact a vitamin C 'complex'. This theory suggests that vitamin C in nature never exists in isolation but always occurs with supporting compounds. Proponents claim this complex includes ingredients such as rutin, bioflavonoids, tyrosine, copper, other trace minerals and various enzymes.
However this marketing concept has several flaws. Scientific research has conclusively shown that ascorbic acid alone is vitamin C, and that pure ascorbic acid by itself can prevent and cure scurvy, the vitamin C deficiency disease (2,5,16,17,18,19,20). While the additional compounds found in natural food sources can be beneficial, they are not part of vitamin C itself (16,17,22,23,24). Plus hospitals successfully treat vitamin C deficiency every day using pure ascorbic acid, not a 'complex' (17).
Are Bioflavonoids Essential With Vitamin C?
Another popular question is that vitamin C is required to be taken with bioflavonoids, natural compounds found in fruits and vegetables, to make it more effective.
In the 1930s, scientists discovered that citrus fruits contained compounds that appeared to strengthen blood vessel walls. These compounds were initially labeled as 'vitamin P' and were thought to work synergistically with vitamin C. This early research, particularly by Nobel laureate Albert Szent-Györgyi, suggested that bioflavonoids could enhance vitamin C's effects on capillary strength and permeability (25).
However subsequent research has shown that vitamin C functions effectively without bioflavonoids, and while they do have their own independent health benefits, pure ascorbic acid alone can prevent and treat vitamin C deficiency (2,5,16,17,18,19,20).
Come join the Puramins journey and embrace the power of purity, quality and integrity for better health every day!
1) European Commission Food and Feed Information Portal Database (https://ec.europa.eu/food/food-feed-portal/screen/health-claims/eu-register)
2) Naidu KA. Vitamin C in human health and disease is still a mystery? An overview. Nutrition Journal. 2003; 2:7. (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC201008/)
3) Cathcart RF. A unique function for ascorbate. Med Hypotheses. 1991. May; 32-7. (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1921774/)
4) Du J, Cullen JJ, Buettner GR. Ascorbic acid: chemistry, biology and the treatment of cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012; Dec;1826(2):443-57. (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22728050/)
5) Moser MA, Chun. Vitamin C and Heart Health: A Review Based on Findings from Epidemiologic Studies. Int J Mol Sci. 2016; Aug 12;17(8):1328. (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5000725/)
6) Rasmussen MP. Vitamin C Evidence for Treating Complications of COVID-19 and other Viral Infections Orthomolecular Medicine News Service, Apr 2020.
(https://www.orthomolecular.org/resources/omns/v16n25.shtml)
7) Cathcart CR. Vitamin C, Titrating to Tolerance. The Vitamin C Foundation. 1994. (https://vitamincfoundation.org/www.orthomed.com/titrate.htm)
8) Fonorow, OR. Unexpected Early Response to Oral Bioavaialbility of Ascorbic Acid. Towsend Letter. 2020. (https://townsendletter.com/unexpected-early-response-to-oral-bioavaialbility-of-ascorbic-acid-foronow-and-hicky/)
9) Levy T. What type of vitamin C supplement is best? (https://www.abundanceandhealth.co.uk/en/blog/post/133-what-type-of-vitamin-c-supplement-is-best-by-dr-levy-md)
10) Maxfield L, Daley SF, Crane JS. Vitamin C Deficiency. StatPearls Publishing; 2023. (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK493187/)
11) Carr AC, et al. Factors Affecting Vitamin C Status and Prevalence of Deficiency: A Global Health Perspective. Nutrients. 2020. (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7400679/)
12) Giannakourou MC, Taoukis PS. Effect of Alternative Preservation Steps and Storage on Vitamin C Stability in Fruit and Vegetable Products. Foods. 2021. (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8619176/)
13) Peake JM. Vitamin C: Effects of Exercise and Requirements with Training. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2003. (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12945825/)
14) U.S. Department of Agriculture, (https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169097/nutrients)
15) Holland and Barrett, Best vitamin C food & drink sources, (https://www.hollandandbarrett.com/the-health-hub/vitamins-and-supplements/vitamins/vitamin-c/best-vitamin-c-fruits-and-veg/)
16) Carr AC, Vissers MC. Synthetic or food-derived vitamin C— Are they equally bioavailable? 2013. Nutrients, 5(11), 4284-4304. (https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/5/11/4284)
17) Fonorow, OR, The Vitamin C Foundation. The Position of the Vitamin C Foundation on Natural Vitamin C and so-called Vitamin C-complex. 2006. (https://vitamincfoundation.org/NaturalC.pdf)
18) Cerullo G, Negro M, Parimbelli M, Pecoraro M, Perna S, Liguori G, Rondanelli M, Cena H, & D'Antona G. The Long History of Vitamin C: From Prevention of the Common Cold to Potential Aid in the Treatment of COVID-19. 2020. Frontiers in immunology, 11, 574029. (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7655735/)
19) Linus Pauling Institute, Oregon State University. The Bioavailability of Different Forms of Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid). (https://lpi.oregonstate.edu/mic/vitamins/vitamin-C/supplemental-forms)
20) Smith, RG. Forms, Doses, and Effects of Vitamins C and E. Orthomolecular Medicine News Service. Apr 2020. (https://orthomolecular.org/resources/omns/v16n26.shtml)
21) Branduardi P, Fossati T, Sauer M, Pagani R, Mattanovich D, Porro D. Biosynthesis of Vitamin C by Yeast Leads to Increased Stress Resistance. 2007. PLoS One. 2007 Oct 31;2(10):e1092 (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2034532/)
22) Office of Dietary Supplements. Vitamin C Fact Sheet for Health Professionals. (https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminCHealthProfessional/)
23) Tan Q, Chen B, Wu C, Shao T. Exploring the potential nutritional role of bioflavonoids in exercise rehabilitation: a kinematic perspective. 2023. Front Nutr. 2023 Jun 30;10:1221800 (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10347382/)
24) Chambial S, Dwivedi S, Shukla KK, John P, Sharma P. Vitamin C in Disease Prevention and Cure: An Overview. 2013. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2013 Sep 1;28(4):314–328. (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3783921/)
25) Szent-Gyoergyi A. Lost in the twentieth century. 1963. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 32:1-15. (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14140702)
